Unix Files And Dirs Managements
赋值文件以及文件夹的指令
1 | |
File Management
查看文件列表:
ls -l
-l: long format
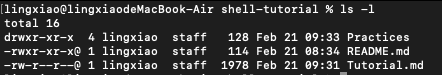
执行命令 ls -l 后,返回的 total 表示目录中所有文件的总块数。这里的 “块” 指的是文件系统中的分配单位,但它并不反映具体文件的大小.
First Column 表示文件类型和权限。
Second Col 表示内存分配的“块”
Third Col 表示文件拥有者
Fourth Col 表示 角色
Fifth Col 表示 文件大小
Sixth Col 表示时间日期
Seventh Col 表示文件名/目录
ls -a
1 | |
在执行
ls -a命令后,会显示包括隐藏文件和目录在内的所有文件和目录。在结果中,你可能会看到以下三个条目:
.DS_Store: 这是 macOS 操作系统中的一个隐藏文件,用于存储与该目录相关的自定义属性和显示选项。它通常用于存储文件夹的自定义图标和排列方式等信息。
. (单个点): 这代表当前目录。在类Unix操作系统中,单个点表示当前工作目录。
… (双点): 这代表上一级目录。在类Unix操作系统中,双点表示当前工作目录的父目录。
这些条目通常是系统生成或维护的,一般用户在正常操作中不需要直接处理它们。在使用
ls -a查看目录内容时,这些隐藏文件和目录也会被列出。
创建编辑文件
vi/vim
ESC : 退出编辑模式
在退出编辑模式时,可以通过(
I:right;h:left,k:up;j:down)方向来移动光标退出编辑模式有两种方法
- ESC – Shit+ZZ
- ESC – wq
显示文件内容
cat filename
1 | |
如果要显示行数 添加-b 选项
1 | |
统计文件单词数量
wc filename
1 | |
1th Col: 总行数o
2th Col: 总单词数量
3th Col: 文件大小
4th Col: filename
复制文件
cp source_file destination_file
执行西面的命令
1 | |
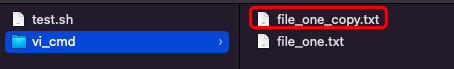
重命名文件
mv old_file new_file
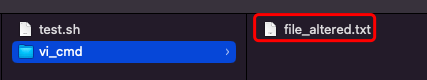
改变之前文件
执行命令之后
1 | |
删除文件
rm filename
注意这种删除方式会直接删除,并不会移动到废纸篓
为了避免误操作,推荐
rm -i
1 | |
Standard Unix Streams
下面的std表示
standard
stdin、stdout 和 stderr 是与程序输入输出相关的三个标准流,它们在操作系统和编程中起到重要的作用。
stdin(标准输入):
- 含义: 表示程序的标准输入流。
- 用途: 程序通过标准输入流接收输入。在大多数情况下,这与用户通过键盘输入相关联。
stdout(标准输出):
- 含义: 表示程序的标准输出流。
- 用途: 程序通过标准输出流产生输出。通常,这与显示结果在屏幕上或将结果输出到文件相关。
stderr(标准错误):
- 含义: 表示程序的标准错误流。
- 用途: 用于输出错误和警告信息。与标准输出不同,标准错误通常用于输出程序运行时的错误消息,以便用户或开发者能够获知程序运行时发生的问题。
Directory Management
查看当前所在目录
pwd
To determine where you are within the filesystem hierarchy at any time, enter the command pwd to print the current working directory
Home Directory
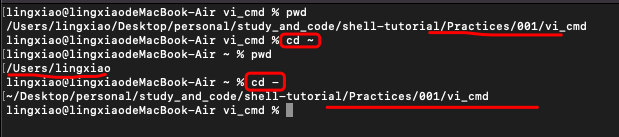
cd ~ : 回到Home目录
You can go in your home directory anytime using the command
cd ~
cd - : To go in last directory
Absolute/Relative Pathnames
- 绝对路径一定是
/开头 - 相对路径一定不是
/开头
创建文件夹
-
创建一个dirname
$ mkdir dirname -
创建多个
$ mkdir dir01 dir02 dir03 -
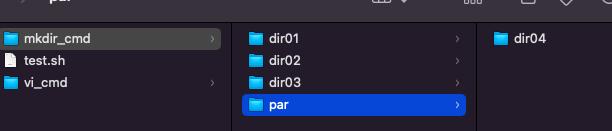
创建父级目录
$ mkdir -p par/dir04
删除文件夹
rmdir directoryName
要保证 将要被删除的是空文件夹
也可以一次性删除多个文件夹,就像创建时一样
重命名文件夹
跟重命名文件一样
File Permission/Access Modes
When execute the ls -l cmd, the results as follows

NOTE:
In the ls -l listing example, every file line begins with a d, -, or l.
The first column represents different access modes. And the first column string’s length is 10.
- The first three characters (2-4) represent the permissions for the file’s owner. For example, -rwxr-xr– represents that the owner has read ®, write (w) and execute (x) permission.
- The second group of three characters (5-7) consists of the permissions for the group to which the file belongs. For example, -rwxr-xr– represents that the group has read ® and execute (x) permission, but no write permission.
- The last group of three characters (8-10) represents the permissions for everyone else. For example, -rwxr-xr– represents that there is read ® only permission.
简言之,
除了第一个字符表示文件还是文件夹之外,后续字符分为三组
- 第一组:(2-4) 表示 文件拥有者的 权限
- 第二组:(5-7) 表示 组 的权限
- 第三组:(8-10)表示所其他人的权限
Changing Permissions
chmod means change mode.
有两种方式该表权限模式
-
The Symbolic Model
-
chmod o+wx testfile
o: 表示其他用户(除了所有者和所属组之外的用户)+: 表示增加权限 -
chmod u-x testfile
u: 表示用户(user)-: 表示移除权限 -
chmod g=rx testfile
g: 代表群组权限。=: 表示赋予权限,而不是添加或移除。
-
-
The Absolute Mode
Number Octal Permission Representation Ref 0 No permission — 1 Execute permission –x 2 Write permission -w- 3 Execute and write permission: 1 (execute) + 2 (write) = 3 -wx 4 Read permission r– 5 Read and execute permission: 4 (read) + 1 (execute) = 5 r-x 6 Read and write permission: 4 (read) + 2 (write) = 6 rw- 7 All permissions: 4 (read) + 2 (write) + 1 (execute) = 7 rwx 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12$ls -l testfile
-rwxrwxr-- 1 amrood users 1024 Nov 2 00:10 testfile
$ chmod 755 testfile
$ls -l testfile
-rwxr-xr-x 1 amrood users 1024 Nov 2 00:10 testfile
$chmod 743 testfile
$ls -l testfile
-rwxr---wx 1 amrood users 1024 Nov 2 00:10 testfile
$chmod 043 testfile
$ls -l testfile
----r---wx 1 amrood users 1024 Nov 2 00:10 testfileNOTE:
chmoe
三个数字filename其中三个数字中 第一个表示 user(owner),第二个表示 group 第三个表示 others
// TODO:
@lingxiao
- To grasp the changing owners and groups in reference link;
- How to change ownership
- SUID and SGID File permisson